Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Miscellaneous
- Protective Effect of Delta-Like 1 Homolog Against Muscular Atrophy in a Mouse Model
- Ji Young Lee, Minyoung Lee, Dong-Hee Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):684-697. Published online August 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1446

- 3,206 View
- 129 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Muscle atrophy is caused by an imbalance between muscle growth and wasting. Delta-like 1 homolog (DLK1), a protein that modulates adipogenesis and muscle development, is a crucial regulator of myogenic programming. Thus, we investigated the effect of exogenous DLK1 on muscular atrophy.
Methods
We used muscular atrophy mouse model induced by dexamethasone (Dex). The mice were randomly divided into three groups: (1) control group, (2) Dex-induced muscle atrophy group, and (3) Dex-induced muscle atrophy group treated with DLK1. The effects of DLK1 were also investigated in an in vitro model using C2C12 myotubes.
Results
Dex-induced muscular atrophy in mice was associated with increased expression of muscle atrophy markers and decreased expression of muscle differentiation markers, while DLK1 treatment attenuated these degenerative changes together with reduced expression of the muscle growth inhibitor, myostatin. In addition, electron microscopy revealed that DLK1 treatment improved mitochondrial dynamics in the Dex-induced atrophy model. In the in vitro model of muscle atrophy, normalized expression of muscle differentiation markers by DLK1 treatment was mitigated by myostatin knockdown, implying that DLK1 attenuates muscle atrophy through the myostatin pathway.
Conclusion
DLK1 treatment inhibited muscular atrophy by suppressing myostatin-driven signaling and improving mitochondrial biogenesis. Thus, DLK1 might be a promising candidate to treat sarcopenia, characterized by muscle atrophy and degeneration.

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
- Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):466-474. Published online June 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1440
- 3,898 View
- 138 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Diabetes is a leading cause of death that is responsible for 1.6 million annual deaths worldwide. However, the life expectancy and age at death of people with diabetes have been a matter of debate.
Methods
The National Health Insurance Service claims database, merged with death records from the National Statistical Information Service in Korea from 2006 to 2018, was analyzed.
Results
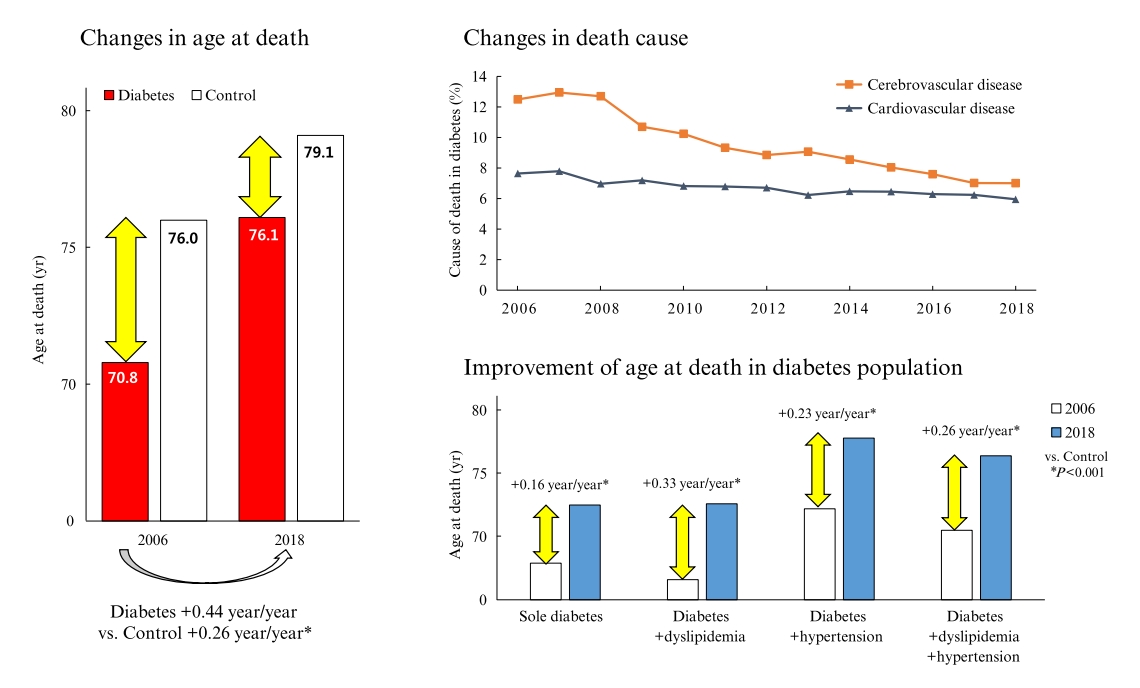
In total, 1,432,567 deaths were collected. The overall age at death increased by 0.44 and 0.26 year/year in the diabetes and control populations, respectively. The disparity in the mean age at death between the diabetes and control populations narrowed from 5.2 years in 2006 to 3.0 years in 2018 (p<0.001). In a subgroup analysis according to the presence of comorbid diseases, the number and proportion of deaths remained steady in the group with diabetes only, but steadily increased in the groups with diabetes combined with dyslipidemia and/or hypertension. Compared to the control population, the increase in the mean death age was higher in the population with diabetes. This trend was more prominent in the groups with dyslipidemia and/or hypertension than in the diabetes only group. Deaths from vascular disease and diabetes decreased, whereas deaths from cancer and pneumonia increased. The decline in the proportion of deaths from vascular disease was greater in the diabetes groups with hypertension and/or dyslipidemia than in the control population.
Conclusion
The age at death in the population with diabetes increased more steeply and reached a comparable level to those without diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Cause-of-Death Mortality in Children and Young Adults with Diabetes: A Nationwide 10-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study
Iee-Ho Choi, Sang-Woo Yeom, Sun-Young Kim, Jihye You, Jong-Seung Kim, Minsun Kim
Children.2023; 10(2): 358. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 770. CrossRef
- Analysis of Cause-of-Death Mortality in Children and Young Adults with Diabetes: A Nationwide 10-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study

- Clinical Study
- Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
- Ji Hong You, Sang Ah Lee, Sung-Youn Chun, Sun Ok Song, Byung-Wan Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Edward J. Boyko
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):901-908. Published online December 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.787
- 6,855 View
- 232 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The aim of this study was to evaluate clinical outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) positive patients with type 2 diabetes compared to those without diabetes in Korea.
Methods
We extracted claims data for patients diagnosed with COVID-19 from the National Health Insurance Service database in Korea from January 20, 2020 to March 31, 2020. We followed up this cohort until death from COVID-19 or discharge from hospital.
Results
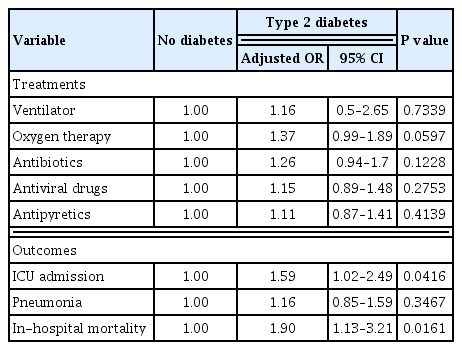
A total of 5,473 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 were analyzed, including 495 with type 2 diabetes and 4,978 without diabetes. Patients with type 2 diabetes were more likely to be treated in the intensive care unit (ICU) (P<0.0001). The incidence of inhospital mortality was higher in patients with type 2 diabetes (P<0.0001). After adjustment for age, sex, insurance status, and comorbidities, odds of ICU admission (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 1.59; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02 to 2.49; P=0.0416) and in-hospital mortality (adjusted OR, 1.90; 95% CI, 1.13 to 3.21; P=0.0161) among patients with COVID-19 infection were significantly higher in those with type 2 diabetes. However, there was no significant difference between patients with and without type 2 diabetes in ventilator, oxygen therapy, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, antipyretics, and the incidence of pneumonia after adjustment.
Conclusion
COVID-19 positive patients with type 2 diabetes had poorer clinical outcomes with higher risk of ICU admission and in-hospital mortality than those without diabetes. Therefore, medical providers need to consider this more serious clinical course when planning and delivering care to type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19 infection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reasons for Hospitalization Among Australians With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024; 48(1): 53. CrossRef - Predictors of COVID-19 outcome in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a hospital-based study
Amira M. Elsayed, Mohamad S. Elsayed, Ahmed E. Mansour, Ahmed W. Mahedy, Eman M. Araby, Maha H. Morsy, Rasha O. Abd Elmoniem
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and Pneumococcal Pneumonia
Catia Cilloniz, Antoni Torres
Diagnostics.2024; 14(8): 859. CrossRef - Risk for Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus after COVID-19 among Korean Adults: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study
Jong Han Choi, Kyoung Min Kim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 245. CrossRef - The Intersection of COVID-19 and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An Overview of the Current Evidence
Mykhailo Buchynskyi, Iryna Kamyshna, Valentyn Oksenych, Nataliia Zavidniuk, Aleksandr Kamyshnyi
Viruses.2023; 15(5): 1072. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Alexander Lang, Nikoletta Christodoulou, Philipp Linnerz, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Manuela Neuenschwander, Janett Barbaresko, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2023; 66(8): 1395. CrossRef - Diabetes and deaths of COVID-19 patients: Systematic review of meta-analyses
Aakriti Garg, Mahesh Kumar Posa, Anoop Kumar
Health Sciences Review.2023; 7: 100099. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and COVID-19 Outcomes in the Asia-Pacific Region: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis and Meta-regression of 84,011 Patients
Ru Ying Fong, Annie Lee, Fei Gao, Jonathan Jiunn Liang Yap, Khung Keong Yeo
Journal of Asian Pacific Society of Cardiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - Factors influencing the severity of COVID-19 course for patients with diabetes mellitus in tashkent: a retrospective cohort study
A. V. Alieva, A. A. Djalilov, F. A. Khaydarova, A. V. Alimov, D. Z. Khalilova, V. A. Talenova, N. U. Alimova, M. D. Aripova, A. S. Sadikova
Obesity and metabolism.2023; 20(2): 92. CrossRef - Genetic Predictors of Comorbid Course of COVID-19 and MAFLD: A Comprehensive Analysis
Mykhailo Buchynskyi, Valentyn Oksenych, Iryna Kamyshna, Sandor G. Vari, Aleksandr Kamyshnyi
Viruses.2023; 15(8): 1724. CrossRef - Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels predict outcome in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Sylvia Mink, Christoph H. Saely, Andreas Leiherer, Matthias Frick, Thomas Plattner, Heinz Drexel, Peter Fraunberger
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Two years of SARS-CoV-2 infection (2019–2021): structural biology, vaccination, and current global situation
Waqar Ahmad, Khadija Shabbiri
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Baseline haemoglobin A1c and the risk of COVID‐19 hospitalization among patients with diabetes in the INSIGHT Clinical Research Network
Jea Young Min, Nicholas Williams, Will Simmons, Samprit Banerjee, Fei Wang, Yongkang Zhang, April B. Reese, Alvin I. Mushlin, James H. Flory
Diabetic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Diabetes and Hyperglycemia on COVID-19 Infection Course—A Narrative Review
Evangelia Tzeravini, Eleftherios Stratigakos, Chris Siafarikas, Anastasios Tentolouris, Nikolaos Tentolouris
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Incidence and Outcomes of COVID-19 Needing Hospital Admission According to Sex: Retrospective Cohort Study Using Hospital Discharge Data in Spain, Year 2020
Jose M. de Miguel-Yanes, Rodrigo Jimenez-Garcia, Javier de Miguel-Diez, Valentin Hernández-Barrera, David Carabantes-Alarcon, Jose J. Zamorano-Leon, Ricardo Omaña-Palanco, Ana Lopez-de-Andres
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2654. CrossRef - The burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(9): 525. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Chinese, Japanese, Korean, US-PIMA Indian, and Trinidadian Screening Scores for Diabetes Risk Assessment and Prediction
Norma Latif Fitriyani, Muhammad Syafrudin, Siti Maghfirotul Ulyah, Ganjar Alfian, Syifa Latif Qolbiyani, Muhammad Anshari
Mathematics.2022; 10(21): 4027. CrossRef - New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus Presenting As Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients With COVID-19: A Case Series
Aysha Sarwani, Mahmood Al Saeed, Husain Taha, Rawdha M Al Fardan
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The management of type 2 diabetes before, during and after Covid-19 infection: what is the evidence?
Leszek Czupryniak, Dror Dicker, Roger Lehmann, Martin Prázný, Guntram Schernthaner
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Reasons for Hospitalization Among Australians With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19

- Clinical Study
- Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data
- Ji Hong You, Sun Ok Song, Se Hee Park, Kyoung Hye Park, Joo Young Nam, Dong Wook Kim, Hyun Min Kim, Dong-Jun Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(3):275-281. Published online September 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.275
- 7,282 View
- 97 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Hyperglycemic crisis is a metabolic emergency associated with diabetes mellitus. However, accurate epidemiologic information on cases of hyperglycemic crisis in Korea remains scarce. We evaluated trends in hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations and in- and out-of-hospital mortality in Korea. We also predicted future trends.
Methods We extracted claims data with hyperglycemic crisis as the principal diagnosis from the National Health Insurance Service database in Korea from January 2004 to December 2013. We investigated the numbers of claims with hyperglycemic crisis and identified trends in hyperglycemic crisis based on those claims data. We predicted future trends by statistical estimation.
Results The total annual number of claims of hyperglycemic crisis increased from 2,674 in 2004 to 5,540 in 2013. Statistical analysis revealed an increasing trend in hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations (
P for trend <0.01). In contrast, the hospitalization rate per 1,000 diabetes cases showed a decreasing trend (P for trend <0.01) during this period. The mortality rate per 1,000 diabetes cases also showed a decreasing trend (P for trend <0.0001). However, no distinct linear trend in the case-related fatality rate at <60 days over the last decade was observed. The predicted number of annual claims of hyperglycemic crisis will increase by 2030.Conclusion The number of hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations in Korea increased in the last decade, although the hospitalization rate per 1,000 diabetes cases and mortality rate decreased. Also, the predicted number of annual claims will increase in the future. Thus, it is necessary to establish long-term healthcare policies to prevent hyperglycemic crisis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing outcome prediction by applying the 2019 WHO DM classification to adults with hyperglycemic crises: A single-center cohort in Thailand
Chatchon Kaewkrasaesin, Weerapat Kositanurit, Phawinpon Chotwanvirat, Nitchakarn Laichuthai
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(4): 103012. CrossRef - Obesity and 30-day case fatality after hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations in Korea: a national cohort study
Hojun Yoon, Hyun Ho Choi, Giwoong Choi, Sun Ok Song, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(3): 74. CrossRef - Interpreting global trends in type 2 diabetes complications and mortality
Mohammed K. Ali, Jonathan Pearson-Stuttard, Elizabeth Selvin, Edward W. Gregg
Diabetologia.2022; 65(1): 3. CrossRef - Comparison of the clinical characteristics and outcomes of pediatric patients with and without diabetic ketoacidosis at the time of type 1 diabetes diagnosis
Young-Jun Seo, Chang Dae Kum, Jung Gi Rho, Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Jin Soon Hwang
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(2): 126. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and outcomes of care in patients hospitalized with diabetic ketoacidosis
Mohsen S. Eledrisi, Haifaa Alkabbani, Malk Aboawon, Aya Ali, Imad Alabdulrazzak, Maab Elhaj, Ashraf Ahmed, Hazim Alqahwachi, Joanne Daghfal, Salem A. Beshyah, Rayaz A. Malik
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 192: 110041. CrossRef - Hyperglycemic Crisis Characteristics and Outcome of Care in Adult Patients without and with a History of Diabetes in Tigrai, Ethiopia: Comparative Study
Getachew Gebremedhin, Fikre Enqueselassie, Helen Yifter, Negussie Deyessa
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 547. CrossRef - Increased Incidence of Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis After COVID-19: A Two-Center Retrospective Study in Korea
Min Jeong Han, Jun Ho Heo
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 783. CrossRef - Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 349. CrossRef - Letter: Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data (Endocrinol Metab 2019;34:275–81, Ji Hong You et al.)
Jang Won Son
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 422. CrossRef - Response: Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data (Endocrinol Metab 2019;34:275–81, Ji Hong You et al.)
Ji Hong You, Sun Ok Song
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 424. CrossRef
- Enhancing outcome prediction by applying the 2019 WHO DM classification to adults with hyperglycemic crises: A single-center cohort in Thailand

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Comparison of the Effects of Ezetimibe-Statin Combination Therapy on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with and without Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
- Namki Hong, Yong-ho Lee, Kenichi Tsujita, Jorge A. Gonzalez, Christopher M. Kramer, Tomas Kovarnik, George N. Kouvelos, Hiromichi Suzuki, Kyungdo Han, Chan Joo Lee, Sung Ha Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(2):219-227. Published online May 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.219
- 5,734 View
- 125 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Ezetimibe-statin combination therapy has been found to reduce low density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) in large trials. We sought to examine the differential effect of ezetimibe on MACEs when added to statins according to the presence of diabetes.
Methods Randomized clinical trials with a sample size of at least 50 participants and at least 24 weeks of follow-up that compared ezetimibe-statin combination therapy with a statin- or placebo-controlled arm and reported at least one MACE, stratified by diabetes status, were included in the meta-analysis and meta-regression.
Results A total of seven trials with 28,191 enrolled patients (mean age, 63.6 years; 75.1% men; 7,298 with diabetes [25.9%]; mean follow-up, 5 years) were analysed. MACEs stratified by diabetes were obtained from the published data (two trials) or through direct contact (five trials). No significant heterogeneity was observed among studies (
I 2=14.7%,P =0.293). Ezetimibe was associated with a greater reduction of MACE risk in subjects with diabetes than in those without diabetes (pooled relative risk, 0.84 vs. 0.93;P heterogeneity=0.012). In the meta-regression analysis, the presence of diabetes was associated with a greater reduction of MACE risk when ezetimibe was added to statins (β=0.87,P =0.038).Conclusion Ezetimibe-statin combination therapy was associated with greater cardiovascular benefits in patients with diabetes than in those without diabetes. Our findings suggest that ezetimibe-statin combination therapy might be a useful strategy in patients with diabetes at a residual risk of MACEs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multifunctional nanoparticle-mediated combining therapy for human diseases
Xiaotong Li, Xiuju Peng, Makhloufi Zoulikha, George Frimpong Boafo, Kosheli Thapa Magar, Yanmin Ju, Wei He
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy and Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination Therapy on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammatory Response in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ji Hye Han, Kyong Hye Joung, Jun Choul Lee, Ok Soon Kim, Sorim Choung, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Hyun Jin Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 112. CrossRef - Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Roh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 55. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Pitavastatin/Ezetimibe Fixed-Dose Combination vs. Pitavastatin: Phase III, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial
Kenichi Tsujita, Koutaro Yokote, Junya Ako, Ryohei Tanigawa, Sachiko Tajima, Hideki Suganami
Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis.2023; 30(11): 1580. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Ezetimibe combination therapy with statin for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an open-label randomized controlled trial (ESSENTIAL study)
Yongin Cho, Hyungjin Rhee, Young-eun Kim, Minyoung Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Jin-Young Choi, Yong-ho Lee
BMC Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - RSSDI consensus recommendations for dyslipidemia management in diabetes mellitus
Banshi Saboo, Sanjay Agarwal, Brij Mohan Makkar, Rajeev Chawla, Sujoy Ghosh, Vijay Viswanathan, Sunil Gupta, Ch. Vasanth Kumar, Anuj Maheshwari, L. Sreenivasamurthy, Rakesh Kumar Sahay, Sanjay Reddy, Shalini Jaggi, Jugal Kishor Sharma, Vijay Panikar, Anan
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(1): 3. CrossRef - Ezetimibe and diabetes mellitus:a new strategy for lowering cholesterol
V.A. Serhiyenko, A.A. Serhiyenko
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(5): 302. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef - Combination of Statin and Ezetimibe versus Statin Monotherapy on Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Incidence among Adults with Impaired Fasting Glucose: a Propensity-Matched Nationwide Cohort Study
You-Bin Lee, Bongsung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jung A Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2021; 10(3): 303. CrossRef - PCSK9 inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes
Daniel Steffens, Peter Bramlage, Céline Scheeff, Mario Kasner, Adel Hassanein, Julian Friebel, Ursula Rauch-Kröhnert
Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy.2020; 20(1): 35. CrossRef - Comparison of Renal Effects of Ezetimibe–Statin Combination versus Statin Monotherapy: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
Jaehyun Bae, Namki Hong, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(3): 798. CrossRef - Effect of Ezetimibe on Glucose Metabolism and Inflammatory Markers in Adipose Tissue
Yongin Cho, Ryeong-Hyeon Kim, Hyunki Park, Hye Jin Wang, Hyangkyu Lee, Eun Seok Kang
Biomedicines.2020; 8(11): 512. CrossRef - Future perspectives of the pharmacological management of diabetic dyslipidemia
Angelo Maria Patti, Rosaria Vincenza Giglio, Nikolaos Papanas, Manfredi Rizzo, Ali A. Rizvi
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2019; 12(2): 129. CrossRef - Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Is It All About Glycemia?
Alessandra Vecchié, Fabrizio Montecucco, Federico Carbone, Franco Dallegri, Aldo Bonaventura
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2019; 25(29): 3112. CrossRef - Triennial Report ofEndocrinology and Metabolism, 2015 to 2017
Eun-Jung Rhee, Hey Yeon Jang, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 195. CrossRef - Guidelines, Clinical Evidence, and Real-Life Practice: How to Find Your Way in Managing Hypercholesterolaemia
Janet Fricker
EMJ Cardiology.2018; : 38. CrossRef
- Multifunctional nanoparticle-mediated combining therapy for human diseases

- Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
- Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):274-280. Published online June 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.274
- 5,250 View
- 175 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Although the beneficial effects of statin treatment in dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis have been well studied, there is limited information regarding the renal effects of statins in diabetic nephropathy. We aimed to investigate whether, and which, statins affected renal function in Asian patients with diabetes.
Methods We enrolled 484 patients with diabetes who received statin treatment for more than 12 months. We included patients treated with moderate-intensity dose statin treatment (atorvastatin 10 to 20 mg/day or rosuvastatin 5 to 10 mg/day). The primary outcome was a change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) during the 12-month statin treatment, and rapid renal decline was defined as a >3% reduction in eGFR in a 1-year period.
Results In both statin treatment groups, patients showed improved serum lipid levels and significantly reduced eGFRs (from 80.3 to 78.8 mL/min/1.73 m2 for atorvastatin [
P =0.012], from 79.1 to 76.1 mL/min/1.73 m2 for rosuvastatin [P =0.001]). A more rapid eGFR decline was observed in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group (48.7% vs. 38.6%,P =0.029). Multiple logistic regression analyses demonstrated more rapid renal function loss in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group after adjustment for other confounding factors (odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.06 to 2.42).Conclusion These results suggest that a moderate-intensity dose of atorvastatin has fewer detrimental effects on renal function than that of rosuvastatin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial
Chan Joo Lee, Woong Chol Kang, Sang Hyun Ihm, Il Suk Sohn, Jong Shin Woo, Jin Won Kim, Soon Jun Hong, Jung Hyun Choi, Jung‐Won Suh, Jae‐Bin Seo, Joon‐Hyung Doh, Jung‐Woo Son, Jae‐Hyeong Park, Ju‐Hee Lee, Young Joon Hong, Jung Ho Heo, Jinho Shin, Seok‐Min
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2024; 26(3): 262. CrossRef - Anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic, and anti-inflammatory effect of the drug Guggulutiktaka ghrita on high-fat diet-induced obese rats
Samreen M. Sheik, Pugazhandhi Bakthavatchalam, Revathi P. Shenoy, Basavaraj S. Hadapad, Deepak Nayak M, Monalisa Biswas, Varashree Bolar Suryakanth
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2022; 13(3): 100583. CrossRef - The challenge of reducing residual cardiovascular risk in patients with chronic kidney disease
Stefan Mark Nidorf
European Heart Journal.2022; 43(46): 4845. CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease in Older People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Improving Prevention and Treatment Options
Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Drugs & Aging.2020; 37(8): 567. CrossRef - Intracellular Mechanism of Rosuvastatin-Induced Decrease in Mature hERG Protein Expression on Membrane
Pan-Feng Feng, Bo Zhang, Lei Zhao, Qing Fang, Yan Liu, Jun-Nan Wang, Xue-Qi Xu, Hui Xue, Yang Li, Cai-Chuan Yan, Xin Zhao, Bao-Xin Li
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2019; 16(4): 1477. CrossRef - The problem of safety of lipid-lowering therapy
M V. Zykov
Kardiologiia.2019; 59(5S): 13. CrossRef - Regional evidence and international recommendations to guide lipid management in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes with special reference to renal dysfunction
Titus WL Lau, Kevin E.K. Tan, Jason C.J. Choo, Tsun‐Gun Ng, Subramaniam Tavintharan, Juliana C.N. Chan
Journal of Diabetes.2018; 10(3): 200. CrossRef - Lipids: a personal view of the past decade
Niki Katsiki, Dimitri P Mikhailidis
Hormones.2018; 17(4): 461. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial

- Clinical Study
- Trends in Diabetes Incidence in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data
- Sun Ok Song, Yong-ho Lee, Dong Wook Kim, Young Duk Song, Joo Young Nam, Kyoung Hye Park, Dae Jung Kim, Seok Won Park, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(2):292-299. Published online June 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.292
- 4,713 View
- 49 Download
- 36 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Epidemiological data is useful to estimate the necessary manpower and resources used for disease control and prevention of prevalent chronic diseases. We aimed to evaluate the incidence of diabetes and identify its trends based on the claims data from the National Health Insurance Service database over the last decade.
Methods We extracted claims data on diabetes as the principal and first additional diagnoses of National Health Insurance from January 2003 to December 2012. We investigated the number of newly claimed subjects with diabetes codes, the number of claims and the demographic characteristics of this population.
Results Total numbers of claimed cases and populations with diabetes continuously increased from 1,377,319 in 2003 to 2,571,067 by 2012. However, the annual number of newly claimed diabetic subjects decreased in the last decade. The total number of new claim patients with diabetes codes decreased as 30.9% over 2005 to 2009. Since 2009, the incidence of new diabetes claim patients has not experienced significant change. The 9-year average incidence rate was 0.98% and 1.01% in men and women, respectively. The data showed an increasing proportion of new diabetic subjects of younger age (<60 years) combined with a sharply decreasing proportion of subjects of older age (≥60 years).
Conclusion There were increasing numbers of newly claimed subjects with diabetes codes of younger age over the last 10 years. This increasing number of diabetic patients will require management throughout their life courses because Korea is rapidly becoming an aging society.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changing landscape of diabetes in Asia – What are the unmet needs?
Andrea OY Luk
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024; 15(4): 402. CrossRef - Risks of colorectal cancer and biliary cancer according to accompanied primary sclerosing cholangitis in Korean patients with ulcerative colitis: a nationwide population-based study
Eun Hye Oh, Ye-Jee Kim, Minju Kim, Seung Ha Park, Tae Oh Kim, Sang Hyoung Park
Intestinal Research.2023; 21(2): 252. CrossRef - The role of nutritional status in the relationship between diabetes and health-related quality of life
Sohyun Park, Sukyoung Jung, Hyunsook Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(4): 505. CrossRef - Lifetime risk of developing diabetes in Chinese people with normoglycemia or prediabetes: A modeling study
Xinge Zhang, Hongjiang Wu, Baoqi Fan, Mai Shi, Eric S. H. Lau, Aimin Yang, Elaine Chow, Alice P. S. Kong, Juliana C. N. Chan, Ronald C. W. Ma, Andrea O. Y. Luk, Claudia Langenberg
PLOS Medicine.2022; 19(7): e1004045. CrossRef - Rising Incidence of Diabetes in Young Adults in South Korea: A National Cohort Study
Hyun Ho Choi, Giwoong Choi, Hojun Yoon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 803. CrossRef - Association between Age-Related Macular Degeneration and the Risk of Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Wonyoung Jung, Je Moon Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Bongseong Kim, Sungsoon Hwang, Dong Hui Lim, Dong Wook Shin
Biomedicines.2022; 10(10): 2435. CrossRef - Relationship between dermatitis and joint replacement: A nationwide population-based cohort study
JoonWoo Jung, Minkook Son, SooHyun Jeong, KwangJoong Kim, KwangHo Kim, EunJoo Park
Indian Journal of Dermatology.2022; 67(3): 312. CrossRef - Prediction of type 2 diabetes using genome-wide polygenic risk score and metabolic profiles: A machine learning analysis of population-based 10-year prospective cohort study
Seok-Ju Hahn, Suhyeon Kim, Young Sik Choi, Junghye Lee, Jihun Kang
eBioMedicine.2022; 86: 104383. CrossRef - A Novel User Utility Score for Diabetes Management Using Tailored Mobile Coaching: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Min-Kyung Lee, Da Young Lee, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2021; 9(2): e17573. CrossRef - Estimating the disease burden of Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients considering its complications
Juyoung Kim, Seok-Jun Yoon, Min-Woo Jo, Brecht Devleesschauwer
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(2): e0246635. CrossRef - Positive association between actinic keratosis and internal malignancies: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Young Bok Lee, Ji Hyun Lee, Yeong Ho Kim, Ji Min Seo, Dong Soo Yu, Yong Gyu Park, Kyung Do Han
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Herpes Zoster and Subsequent Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Miri Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung Ah Yoo, Ji Hyun Lee
Dermatology.2021; 237(1): 73. CrossRef - Identification of herpes zoster high‐risk group using Charlson comorbidity index: A nationwide retrospective cohort study
Soo Ick Cho, Dong Hun Lee, Young Min Park
The Journal of Dermatology.2020; 47(1): 47. CrossRef - Increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease in patients with psoriasis: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Miri Kim, Hyo Eun Park, Si-Hyung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Ji Hyun Lee
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The incidence rates and risk factors of Parkinson disease in patients with psoriasis: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Ji Hyun Lee, Kyungdo Han, Heon Yung Gee
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.2020; 83(6): 1688. CrossRef - Site-specific cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea
Suk Kyeong Kim, Ju-Young Jang, Dong-Lim Kim, Young A Rhyu, Suh Eun Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Kee-Ho Song
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 35(3): 641. CrossRef - Secular trends in incidence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in Hong Kong: A retrospective cohort study
Andrea O. Y. Luk, Calvin Ke, Eric S. H. Lau, Hongjiang Wu, William Goggins, Ronald C. W. Ma, Elaine Chow, Alice P. S. Kong, Wing-Yee So, Juliana C. N. Chan, Sanjay Basu
PLOS Medicine.2020; 17(2): e1003052. CrossRef - Long‐term risk of congestive heart failure in younger breast cancer survivors: A nationwide study by the SMARTSHIP group
Jihyoun Lee, Ho Hur, Jong Won Lee, Hyun Jo Youn, Kyungdo Han, Nam Won Kim, So‐Youn Jung, Zisun Kim, Ku Sang Kim, Min Hyuk Lee, Se‐Hwan Han, Sung Hoo Jung, Il Yong Chung
Cancer.2020; 126(1): 181. CrossRef - The Lancet Commission on diabetes: using data to transform diabetes care and patient lives
Juliana C N Chan, Lee-Ling Lim, Nicholas J Wareham, Jonathan E Shaw, Trevor J Orchard, Ping Zhang, Eric S H Lau, Björn Eliasson, Alice P S Kong, Majid Ezzati, Carlos A Aguilar-Salinas, Margaret McGill, Naomi S Levitt, Guang Ning, Wing-Yee So, Jean Adams,
The Lancet.2020; 396(10267): 2019. CrossRef - Prognosis of Patients with Colorectal Cancer with Diabetes According to Medication Adherence: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Sunho Choe, Joonki Lee, Ji Won Park, Seung-Yong Jeong, Young Min Cho, Byung-Joo Park, Aesun Shin
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2020; 29(6): 1120. CrossRef - Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data
Ji Hong You, Sun Ok Song, Se Hee Park, Kyoung Hye Park, Joo Young Nam, Dong Wook Kim, Hyun Min Kim, Dong-Jun Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 275. CrossRef - Response: Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data (Endocrinol Metab 2019;34:275–81, Ji Hong You et al.)
Ji Hong You, Sun Ok Song
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 424. CrossRef - A simple screening score to predict diabetes in cancer patients
Ji-Su Kim, Sun-Hye Ko, Myong Ki Baeg, Kyung-Do Han
Medicine.2019; 98(51): e18354. CrossRef - Cancer risk in 892 089 patients with psoriasis in Korea: A nationwide population‐based cohort study
Ji Hyun Lee, Hyo Jung Kim, Kyung Do Han, Ha‐Na Kim, Young Min Park, Jun Young Lee, Yong‐Gyu Park, Young Bok Lee
The Journal of Dermatology.2019; 46(2): 95. CrossRef - Effects of sarpogrelate on microvascular complications with type 2 diabetes
Hyunju Yoo, Inwhee Park, Dae Jung Kim, Sukhyang Lee
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2019; 41(2): 563. CrossRef - Presence of Metabolic Syndrome Components Is Associated with Tooth Loss in Middle-Aged Adults
Min-Jeong Cho, Youn-Hee Choi, Hyeon Chang Kim, Jee-Seon Shim, Atsuo Amano, Ji-Young Kim, Keun-Bae Song
Yonsei Medical Journal.2019; 60(6): 554. CrossRef - Ten-Year Mortality Trends for Adults with and without Diabetes Mellitus in South Korea, 2003 to 2013
Kyeong Jin Kim, Tae Yeon Kwon, Sungwook Yu, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Dong Seop Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Yousung Park, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 394. CrossRef - Cancer risk by the subtype of alopecia
Ji Hyun Lee, Yumee Song, Kyung Do Han, Young Min Park, Jun Young Lee, Yong-Gyu Park, Young Bok Lee
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Nationwide Analysis of Treatment Patterns for Korean Breast Cancer Survivors Using National Health Insurance Service Data
Il Yong Chung, Jihyoun Lee, Suyeon Park, Jong Won Lee, Hyun Jo Youn, Jung Hwa Hong, Ho Hur
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center (CMERC) cohort: study protocol and results of the first 3 years of enrollment
Jee-Seon Shim, Bo Mi Song, Jung Hyun Lee, Seung Won Lee, Ji Hye Park, Dong Phil Choi, Myung Ha Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungha Park, Won-Woo Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2017; 39: e2017016. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Vildagliptin in Clinical Practice: Pooled Analysis of Three Korean Observational Studies (the VICTORY Study)
Sunghwan Suh, Sun Ok Song, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hyungjin Cho, Woo Je Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Effects of Lobeglitazone, a Novel Thiazolidinedione, on Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus over 52 Weeks
Soo Lim, Kyoung Min Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Doo Man Kim, Jeong-Taek Woo, Choon Hee Chung, Kyung Soo Ko, Jeong Hyun Park, Yongsoo Park, Sang Jin Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Dong Seop Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 377. CrossRef - Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(5): 845. CrossRef
- Changing landscape of diabetes in Asia – What are the unmet needs?

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Optimal Candidates for the Switch from Glimepiride to Sitagliptin to Reduce Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hyun Min Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun-Seok Kang, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong-Soo Cha
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):84-91. Published online March 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.84
- 5,864 View
- 98 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Sitagliptin is a novel antidiabetic agent with a low risk for hypoglycemia. We investigated the efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when patients switched from a sulfonylurea to sitagliptin and identified good candidates for the switch.
Methods Sixty-one patients with type 2 diabetes switched from glimepiride with metformin to sitagliptin with metformin due to clinical hypoglycemia. Serum glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and 2-hour postprandial plasma glucose (2h-PPG) before and 12 and 24 weeks after the drug switch were checked.
Results HbA1c and FPG levels did not change 12 or 24 weeks after the switch; however, the 2h-PPG level decreased from 218.0±67.5 mg/dL at baseline to 197.1±69.9 mg/dL at 12 weeks and 192.3±67.4 mg/dL at 24 weeks after switching drugs (
P =0.045,P =0.018, respectively). All but one patient no longer experienced hypoglycemia after discontinuing glimepiride. In a multivariate logistic regression analysis, a high homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance and low baseline HbA1c level were independent predictors of an HbA1c ≤7% after switching to sitagliptin.Conclusion Glycemic control was not aggravated in patients 24 weeks after the drug switch, and symptomatic hypoglycemia decreased significantly. Patients with dominant insulin resistance may be good candidates for switching from a sulfonylurea to sitagliptin to reduce hypoglycemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of Machine Learning Methods for the Development of Antidiabetic
Drugs
Juanjuan Zhao, Pengcheng Xu, Xiujuan Liu, Xiaobo Ji, Minjie Li, Dev Sooranna, Xiaosheng Qu, Wencong Lu, Bing Niu
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2022; 28(4): 260. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of dorzagliatin for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
Yunfeng Yu, Xingyu Yang, Keke Tong, Shuang Yin, Gang Hu, Fei Zhang, Pengfei Jiang, Manli Zhou, Weixiong Jian
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with switching from sulphonylureas to dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors among patients with type 2 diabetes in the United States
Xi Tan, Lingfeng Yang, Kamlesh Khunti, Ruya Zhang, Ye Zhang, Swapnil Rajpathak, Miao Yu
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(10): 2251. CrossRef - Increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events by strict glycemic control after percutaneous coronary intervention (HbA1c < 6.5% at 2 years) in type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with acute coronary syndrome: a 5-years follow-up study
Tiangui Yang, Peng Fu, Jie Chen, Xi Fu, Changlu Xu, Xiaoxia Liu, Tiesheng Niu
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2021; 37(9): 1517. CrossRef - Clinical analysis of pre-existing diabetes mellitus and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in patients with remitting seronegative symmetrical synovitis and pitting edema syndrome
Yoshiro Horai, Tomoki Origuchi, Nozomi Iwanaga, Junichi Tokumitsu, Toshiyuki Ikeoka, Genpei Kuriya, Yasumori Izumi, Atsushi Kawakami
Modern Rheumatology.2020; 30(4): 703. CrossRef - The efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of 58 randomized controlled trials
Juan Ling, Peng Cheng, Long Ge, Ding-hua Zhang, An-chen Shi, Jin-hui Tian, Ya-jing Chen, Xiu-xia Li, Jing-yun Zhang, Ke-hu Yang
Acta Diabetologica.2019; 56(3): 249. CrossRef - Satisfaction and efficacy of switching from daily dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors to weekly trelagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes—Randomized controlled study—
Mayuko Oita, Hideaki Miyoshi, Kota Ono, Akinobu Nakamura, Kyu Yong Cho, Hiroshi Nomoto, Kohei Yamamoto, Kazuno Omori, Naoki Manda, Yoshio Kurihara, Shin Aoki, Tatsuya Atsumi
Endocrine Journal.2018; 65(2): 141. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of evogliptin versus sitagliptin as add on to metformin alone in a combined russian-korean population. Evo-combi trial
Alina Y. Babenko, Anna A. Mosikian, Igor E. Makarenko, Victoriya V. Leusheva, Evgeny V. Shlyakhto
Diabetes mellitus.2018; 21(4): 241. CrossRef - Effectiveness prediction of Evogliptin treatment in type 2 diabetes mellitus in russian-korean population
Anna A. Mosikian, Alina Y. Babenko, Yulia A. Sevastyanova, Roman V. Drai, Evgenij V. Shlyakhto
Diabetes mellitus.2018; 21(5): 333. CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis of the Co-structures of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its inhibitor
Hiroyuki Nojima, Kazuhiko Kanou, Genki Terashi, Mayuko Takeda-Shitaka, Gaku Inoue, Koichiro Atsuda, Chihiro Itoh, Chie Iguchi, Hajime Matsubara
BMC Structural Biology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - A genetic variant in GLP1R is associated with response to DPP-4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes
Eugene Han, Hye Sun Park, Obin Kwon, Eun Yeong Choe, Hye Jin Wang, Yong-ho Lee, Sang-Hak Lee, Chul Hoon Kim, Lee-Kyung Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Chul Sik Kim, Eun Seok Kang
Medicine.2016; 95(44): e5155. CrossRef
- Application of Machine Learning Methods for the Development of Antidiabetic
Drugs


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



